Disclosure
This post contains affiliate links. If you click and buy, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thanks for supporting our website!
Introduction to the Scrum Career Compass
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly adopting Agile methodologies to stay competitive and deliver value faster. Among these methodologies, Scrum has emerged as the most widely implemented Agile framework. Whether you’re an aspiring Scrum Master, a Product Owner, or an Agile Coach, understanding the “Scrum Career Compass” can significantly enhance your journey through the Agile career landscape. This comprehensive guide will provide you with actionable insights, a structured career roadmap, certifications to consider, essential skills to develop, and practical steps to advance your career in Scrum.
Chapter 1: What is Scrum?
Scrum is an Agile framework for managing complex projects. It emphasizes collaboration, accountability, and iterative progress toward well-defined goals. Scrum is structured around a small team of people, the Scrum Team, consisting of a Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Developers.
Key principles of Scrum include:
- Empiricism (transparency, inspection, adaptation)
- Iterative progress via Sprints
- Defined roles and responsibilities
- Continuous improvement via Sprint Retrospectives
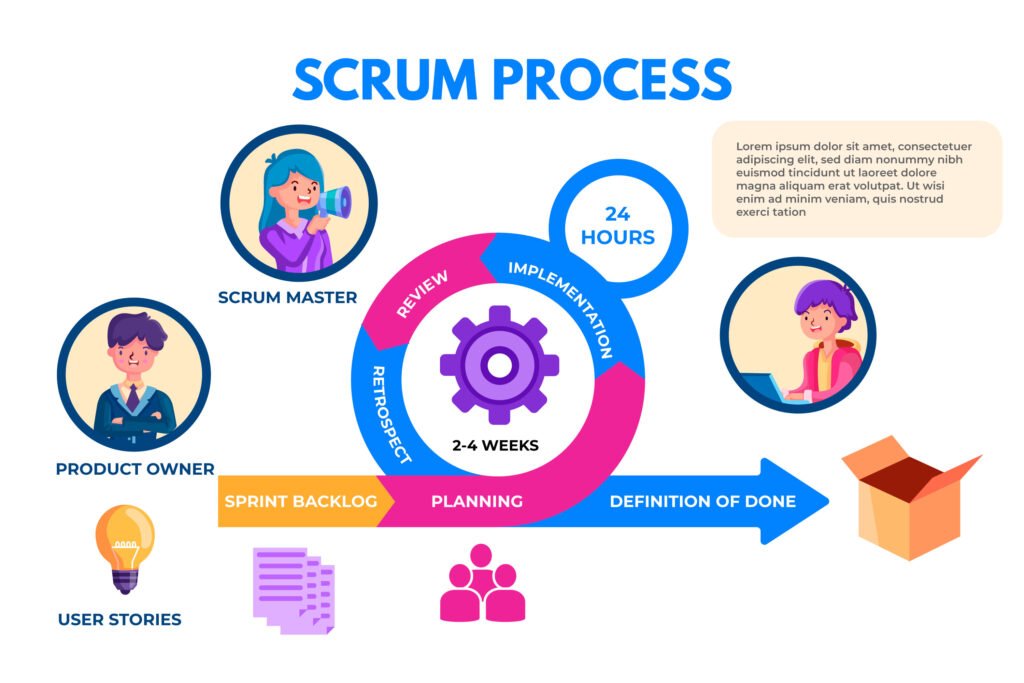
Scrum promotes flexibility and encourages teams to deliver incremental improvements. This ability to quickly adapt is what makes it appealing to tech startups, government institutions, and large enterprises alike.
Chapter 2: Understanding the Scrum Career Compass
The Scrum Career Compass is a conceptual framework designed to guide professionals at any level through their journey in Scrum and Agile careers. It helps:
- Identify suitable roles based on current skills and interests
- Suggest professional certifications and learning paths
- Outline career progression opportunities
- Provide strategic advice for long-term career growth
The compass points toward four primary Scrum career tracks:
- Scrum Master Track
- Product Owner Track
- Agile Coaching Track
- Development Team Specialist Track
Each direction offers unique challenges, growth opportunities, and required competencies.

Each of these tracks aligns with key business needs. While Scrum Masters focus on process, Product Owners concentrate on value, Developers bring technical solutions to life, and Agile Coaches help build sustainable Agile cultures.
Chapter 3: Scrum Career Compass – Scrum Master Track
Role Overview
A Scrum Master serves as a facilitator for the Scrum Team. They ensure the team adheres to Scrum principles, removes impediments, and coaches team members toward Agile maturity.
Career Progression
- Entry-Level: Junior Scrum Master
- Mid-Level: Scrum Master
- Senior-Level: Senior Scrum Master or Agile Project Manager
- Expert-Level: Agile Coach or Enterprise Agile Coach
Recommended Certifications
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) by Scrum Alliance
- Professional Scrum Master (PSM I, II, III) by Scrum.org
- Safe Scrum Master (SSM) for enterprise-level implementation
Skills to Develop
- Servant leadership
- Facilitation and conflict resolution
- Agile coaching
- Agile metrics and reporting
Scrum Masters are increasingly being recognized not just as team-level facilitators but as key influencers in organizational change. Advanced practitioners often engage in enterprise coaching or transformation initiatives.
Chapter 4: Scrum Career Compass – Product Owner Track
Role Overview
The Product Owner maximizes the value of the product resulting from the work of the Scrum Team. They manage the Product Backlog, ensure stakeholder alignment, and prioritize work based on business value.
Career Progression
- Entry-Level: Associate Product Owner
- Mid-Level: Product Owner
- Senior-Level: Senior Product Owner or Product Manager
- Expert-Level: Chief Product Owner or Head of Product
Recommended Certifications
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO)
- Professional Scrum Product Owner (PSPO I, II)
- Safe Product Owner/Product Manager (POPM)
Skills to Develop
- Business analysis
- Stakeholder management
- Product lifecycle management
- Data-driven decision-making
The Product Owner is critical to delivering customer satisfaction and strategic alignment. A well-trained PO balances technical input, user needs, and company vision to create competitive products.

Chapter 5: Scrum Career Compass – Agile Coaching Track
Role Overview
Agile Coaches mentor individuals, teams, and organizations in Agile practices. They drive Agile transformations and build a culture of continuous improvement.
Career Progression
- Entry-Level: Agile Practitioner or Senior Scrum Master
- Mid-Level: Team Coach
- Senior-Level: Agile Coach
- Expert-Level: Enterprise Agile Coach or Transformation Lead
Recommended Certifications
- ICAgile Certified Professional in Agile Coaching (ICP-ACC)
- Certified Agile Coach (ICP-CAT)
- Safe Program Consultant (SPC)
Skills to Develop
- Systems thinking
- Change management
- Coaching and mentoring
- Organizational design
As organizations seek to scale Agile, Agile Coaches are becoming more in demand. These roles often require deep emotional intelligence, empathy, and an understanding of organizational psychology.

Scrum Career Compass – Developer Track
Role Overview
While often overlooked in Scrum discussions, Developers play a critical role. Scrum Developers are responsible for delivering potentially shippable increments of the product at the end of each Sprint.
Career Progression
- Entry-Level: Junior Developer
- Mid-Level: Scrum Developer
- Senior-Level: Senior Developer or Technical Lead
- Expert-Level: Solutions Architect or DevOps Engineer
Recommended Certifications
- Professional Scrum Developer (PSD)
- AWS/GCP/Azure certifications for DevOps and cloud expertise
- Advanced programming and system architecture courses
Skills to Develop
- TDD/BDD practices
- CI/CD pipeline management
- Pair programming and mob programming
- Test automation
High-performing developers in Scrum environments often evolve into tech leads or solution architects. They also play a key role in DevOps transformation and Agile engineering practices.

Chapter 7: Choosing Your Direction with the Scrum Career Compass
Choosing the right direction in the Scrum Career Compass depends on:
- Personal interests: Are you people-focused or technology-focused?
- Strengths: Do you excel at facilitation, analysis, or development?
- Career goals: Do you aspire to lead, coach, or innovate?
Consider experimenting with cross-functional roles before committing. Job shadowing, volunteering for Scrum roles, or taking short-term certifications can help clarify your path.
A self-assessment combined with feedback from mentors or Agile coaches can offer clarity. Think of your career like a product backlog—constantly refined.
Chapter 8: Scrum Career Compass Guide to Building a Strong Portfolio
To stand out in the Agile job market, build a strong Scrum career portfolio that includes:
- Real-world project experience
- Documented retrospectives and lessons learned
- Contributions to Agile communities
- Case studies or write-ups of Agile transformations you’ve been part of
- Testimonials or endorsements from peers
Also consider maintaining a blog or public profile where you share your insights, Agile experiments, or lessons learned. This demonstrates your continuous learning mindset.
Chapter 9: Using the Scrum Career Compass to Grow Your Agile Network
Engaging with the Scrum and Agile community is essential for career growth:
- Attend Agile conferences (e.g., Agile Alliance, Scrum.org Global Events)
- Join local or online meetups
- Contribute to open-source Agile projects
- Share insights on LinkedIn or Medium
These activities can elevate your profile and connect you with mentors, job opportunities, and industry trends.
Networking is not just about job hunting—it’s about learning from others, building your brand, and staying on the cutting edge of Agile thinking.

Chapter 10: Evolving with the Scrum Career Compass – 2025 Trends
The Scrum Career Compass continues to evolve as Agile practices mature. Key trends to watch include:
- Greater emphasis on Agile leadership and organizational agility
- Blending of Scrum with DevOps and Design Thinking
- Increasing demand for remote Agile facilitation skills
- Rise of AI-powered Scrum tools for backlog prioritization and Sprint planning
Organizations are also shifting toward outcome-based metrics over velocity or output, which changes how Scrum teams measure success.
Conclusion: Aligning Your Career Path with the Scrum Career Compass
The Scrum Career Compass is not just a directional tool; it’s a mindset. It helps professionals reflect on where they are, where they want to go, and how they can get there by leveraging the principles of Scrum.
With a strategic approach to certifications, skills development, community engagement, and career mapping, you can confidently navigate your path in the world of Agile. Let the Scrum Career Compass be your guide to not just a job—but a fulfilling and impactful career.

Additional SEO Keywords:
- Scrum career path
- Agile certification roadmap
- Scrum Master career guide
- Product Owner career journey
- Agile coaching certification
- Scrum career development
- Entry-level Scrum roles
- Professional Scrum guide
Meta Description: Discover your ideal Scrum career path using the Scrum Career Compass. This complete guide explores roles, certifications, and strategies to thrive in Agile project management.


